Mikrotik Routeros V6.0 X86 (level 6 License) Vmware Image
- Mikrotik Routeros V6.0 X86 (level 6 License) Vmware Imagenes
- Mikrotik Routeros V6.0 X86 (level 6 License) Vmware Image Download
We are releasing a test version of an exciting new feature - Cloud Hosted Router (CHR). It is a Virtual Machine image of RouterOS that has full functionality of RouterOS without any kind of conventional RouterOS license, with the limitation of 1Mbit per interface, in future, we will offer unlimited speed with a paid subscription. Mikrotik License Crack. Mikrotik Cracked V.5.20 + License Key Level 6. OS Mikrotik RouterOS - Download Mikrotik RouterOS for. Mikrotik routeros 6 crack - Google Docs 60 2 report mikrotik routeros v6.0 x86 level 6 license. Video tutorial how crack license level 6 mikrotik 5 24 with huntertik 2 3 1. MikroTik RouterOS Level 4 License Key – PC/X86 Systems Only SKU: MT-KEY86-L4. (Supplier Stock Code: MT-KEY86-L4 ) Categories: Broadband Wireless, MikroTik, RouterOS Licenses. MikroTik 6 License Key Generator Download. MikroTik 6 License Key Generator is a Windows supported Linux Kernel Once installation of this program on computer, it’ll amendment your computer on the router that comes with necessary options MikroTik 6 MikroTik 6 License Key Generator is a Latvian organization that was supported in 1995 to supply for advanced routers and wireless ISP.
Mikrotik Routeros V6 0 X86 Level 6 License Vmware Image
Installing routeros on an x86 machine is very simple pc: download the iso image, burn it to cd and boot from it. your new router will run for 24 hours without a license (turn it off to stop the timer). during this time you can try all the features of routeros. Mikrotik is a latvian company which was founded in 1996 to develop routers and wireless isp systems. mikrotik now provides hardware and software for internet connectivity in most of the countries around the world. Mikrotik routeros x86 firmware 6.41 rc 38 2017 10 03; mikrotik routeros x86 firmware 6.40.4 2017 10 03; mikrotik routeros x86 firmware 6.41 rc 3 2017 10 02; mikrotik routeros x86 firmware 6.41 rc 34 2017 09 28; mikrotik routeros x86 firmware 6.41 rc 32 2017 09 26; mikrotik routeros x86. Download mikrotik routeros x86 firmware 6.46.8 (router switch ap) important note!!! the dude server must be updated to monitor v6.46.4 and v6.47beta30 routeros type devices. Mikrotik cloud hosted router (chr) is a routeros version intended to be used as a virtual machine instance. it runs on x86 64 bit architecture and can be deployed on most hypervisors such as: vmware, esxi, player and workstation.
Configurar Mikrotik Routeros X86 Medio Video Online
Routeros. wireless networking. mikrotik x86 compatible wireless . espetoet. just joined. posts: 1 joined: thu nov 21, 2019 4:39 pm. mikrotik x86 compatible wireless. thu nov 21, 2019 4:52 pm. hello, i am trying to mount compatible hardware with mikrotik x86. configuration i have, motherboard: intel dq77kb processor: intel xeon e3 1260l. Mikrotik hardware routers that run routeros come preinstalled with a routeros license, if you have purchased a routeros based device, nothing must be done regarding the license. for x86 systems (i.e. pc devices), you need to obtain a license key. F40dba8b6f you can try routeros on your pc (x86) platform. download iso image from mikrotik download section and install it on pc platform to get softid why use cracked version of routeros 2.9.6 when you can use full version of latest routeros 6.18 iso full mikrotik 6.18 full crack key level 6. Mikrotik routeros is the operating system of mikrotik routerboard hardware. it can also be installed on a pc and will turn it into a router with all the necessary features routing, firewall, bandwidth management, wireless access point, backhaul link, hotspot gateway, vpn server and more. You can try routeros on your pc (x86) platform. download iso image from mikrotik download section and install it on pc platform to get softid once you download the iso image you can read our installation guide. on the same pages, you can download cloud hosted router.vmdk,.vhdx,.vdi and raw disk image files.
Install Mikrotik Os On Pc (mikrotik Pc Router)
Mikrotik 7beta4 crack incl license 100 keygen win x64 x32. for x86 systems (ie. pc devices), you need to obtain a license key. the license key is a block of symbols that needs to be copied from your mikrotik account, or from the email you received in, and then it can be pasted into the router. cloud hosted router (chr) licenses for virtual machines do not use levels,. 60 day free trial license. Mikrotik routeros is the stand alone operating system of mikrotik routerboard hardware. it can also be installed on a pc and will turn it into a router with all the necessary features routing, firewall, bandwidth, management, wireless access point, backhaul link, hotspot, gateway, vpn server and more. Routeros features. routeros is mikrotik's stand alone operating system based on linux v3.3.5 kernel. the following list shows features found in the latest routeros release: hardware support. i386 compatible architecture smp – multi core and multi cpu compatible. Cloud hosted router cloud hosted router (chr) is a routeros version intended for running as a virtual machine. it supports the x86 64 bit architecture and can be used on most of the popular hypervisors such as vmware, hyper v, virtualbox, kvm and others. Mikrotik devices are preinstalled with routeros, so installation is usually not needed, except in the case where installing routeros on an x86 pc. the upgrade procedure on already installed devices is straight forward.
Related image with mikrotik routeros x86
Related image with mikrotik routeros x86
MikroTikRouterOS is the stand-alone operating system of MikroTik RouterBOARD hardware. It can also be installed on a PC and will turn it into a router with all the necessary features - routing, firewall, bandwidth, management, wireless access point, backhaul link, hotspot, gateway, VPN server and more.
The tutorial explains how to install RouterOS on Qemu virtual disk and configure GNS3 software to run such a router. Later, We will use GNS3 to a create simple testing topology with one RoutersOS router connected to emulated Cisco 3725 router.
You can download Mikrotik RouterOS x86 installed on Qemu and VirtualBox images in the Download section here.
Software Prerequisites
- GNS3 with Qemu or VirtualBox support
- Qemu or VirtualBox
- RouterOS ISO image - mikrotik-6.37.5.iso
Virtual Machine Prerequisites
- i386 compatible architecture
- minimum 32MB of RAM (maximum supported 2GB)
- minimum Hard Disk space 64MB
- Network cards supported by linux v3.3.5 kernel (PCI, PCI-X)
RouterOS x86 Installation
1. Download RouterOS for x86 Architecture
$ wget https://download2.mikrotik.com/routeros/6.37.5/mikrotik-6.37.5.iso
2. Create Qemu Virtual Disk and Start Virtual Machine
$ /usr/local/bin/qemu-img create -f qcow2 routeros-6.37.5.img 200M
$ /usr/local/bin/qemu-system-i386 -m 512 -enable-kvm -boot d -cdrom mikrotik-6.37.5.iso routeros-6.37.5.img
3. Install RouterOS
Use spacebar to select packages that are needed. Then press 'i' to install RouterOS.
Picture 1 - RouterOS Installation
Once RouterOS is installed, you have 24 hours to enter a license key to activate RouterOS Qemu image. The timer stops if router is shutdowned. For this reason, we let GNS3 automatically create the copy of base Qemu image every time is a new RouterOS instance placed on the GNS3 desktop. These independent copy of the base image can be run for total 24 hours time period.
4. Start RouterOS Qemu Disk
After the disk is formatted and packages copied, start RouterOS instance with the command:
$ /usr/local/bin/qemu-system-i386 -m 512 -enable-kvm -boot c routeros-6.37.5.img -nographic -serial telnet::4444,server,nowait
You should be able to login to RouterOS with the telnet command:
$ telnet 127.0.0.1 4444
Username is admin without password set.

5. Connect Qemu image to GNS3
I assume that GNS3 is correctly installed and configured.
a) Start GNS3 and create a new GNS3 project
Picture 2 - Creating GNS3 New Project
b) Configure Qemu guest settings
Navigate to Edit -> Preferences -> Qemu -> Qemu Guest and configure parameters as it is shown on the picture below.
Mikrotik Routeros V6.0 X86 (level 6 License) Vmware Imagenes
Picture 3 - Qemu Guest Settings
RouterOS Configuration
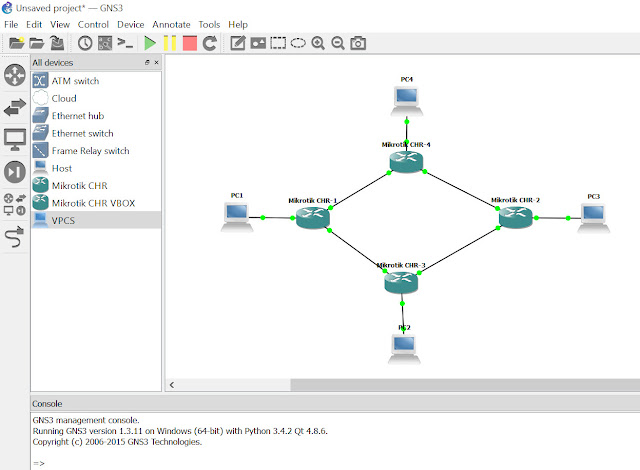
1. Testing Topology
The topology consists of one RouterOS that connects two Microcore Qemu instances. As we want to test switching and VLANs, both Microcore instances are connected to RouterOS switvchport that are separated by VLANs - VLAN10 and VLAN20.
RouterOS's interface Ethernet1 si connected to Cisco 3725 router emulated by Dynamips. The port will be configured as a trunk port on RouterOS side and as a routed port with two sub-interfaces on Cisco's side.
Picture 4 - Testing Topology
2. Create Bridges for VLAN10 and VLAN20 and Assign Access Ports to Bridges
First, check available Ethernet interfaces.They are six Ethernet interfaces presented in RouterOS console in total.
Picture 5 - Router Ethernet Interfaces
We are going to create bridges br10 and br20 and assign interface Ethernet2 to the bridge br10 and Ethernet3 to br20.
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface bridge add name=br10
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface bridge add name=br20
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface bridge port add interface=ether2 bridge=br10
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface bridge port add interface=ether3 bridge=br20
3. Configure Trunk Port to allow VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 and create Switched Virtual Interfaces - SVI10 and SVI20
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface vlan add vlan-id=10 name=SVI10 interface=ether1 disabled=no
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface vlan add vlan-id=20 name=SVI20 interface=ether1 disabled=no
Note: the term SVI is used in a Cisco world, feel free to change it if you want.
4. Add SVI Ports to Bridges
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface bridge port add interface=SVI10 bridge=br10 disabled=no
[admin@MikroTik] > /interface bridge port add interface=SVI20 bridge=br20 disabled=no
Picture 6 - Bridge Ports Configuration
5. Assign IP address to SVI Ports
This configuration ensures that intervlan routing betwwen VLAN 10 and VLAN20 can be done by RouterOS.
[admin@MikroTik] > /ip address add interface=SVI10 address=192.168.10.254/24 disabled=no
[admin@MikroTik] > /ip address add interface=SVI20 address=192.168.20.254/24 disabled=no
At this point you should be able to make successful ping between PC1 and PC2.
6. Set password and hostname
[admin@MikroTik] > /password new-password=admin
[admin@MikroTik] > /system identity set name=RouterOS-I
7. Static routing configuration
[admin@RouterOS-I] > /ip route add dst-address=10.10.10.10/32 gateway=192.168.10.253
Picture 7 - Routing Table
End hosts PC1 and PC2 Configuration
End hosts are represent by Microcore Linux 3.8.2 installed on Qemu virtual disks. Ethernet interfaces configuration is stored in the file /opt/bootlocal.sh that is started during the boot of Microcore. To save configuration changes, the script /usr/bin/filetool.sh must be called with parameter -b.
PC1
tc@box:~$ sudo su
root@tc:# echo 'ifconfig eth0 192.168.10.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 up' >> /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@tc:# echo 'hostname PC2' >> /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@tc:# echo 'route add default gw 192.168.10.254' >> /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@tc:~# /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@PC1:~# /usr/bin/filetool.sh -b
PC2
tc@box:~$ sudo su
root@tc:# echo 'ifconfig eth0 192.168.20.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 up' >> /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@tc:# echo 'hostname PC2' >> /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@tc:# echo 'route add default gw 192.168.20.254' >> /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@tc:~# /opt/bootlocal.sh
root@PC2:~# /usr/bin/filetool.sh -b
Cisco 3725 Configuration
1. Router-on-the-stick Configuration
3725#conf t
3725(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
3725(config-if)#no shut
3725(config-if)#exit

3725(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/0.10
3725(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1Q 10
3725(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.10.253 255.255.255.0
3725(config-subif)#no shutdown
3725(config-subif)#int fa0/0.20
3725(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1Q 20
3725(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.20.253 255.255.255.0
3725(config-subif)#no shutdown
Mikrotik Routeros V6.0 X86 (level 6 License) Vmware Image Download
2. Loopback configuration
725(config)#interface loopback 0
3725(config-if)#ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255
3725(config-if)#no shutdown
Testing Connectivity
1. Check if RouterOS does Packet Switching Between VLAN10 and VLAN20 Subnets
Issue the command ping on PC1 to test connectivity between PC1 and PC2.
Picture 8 - RouterOS InterVlan Routing
2. Check if VLAN Tagged Traffic is Transferred via Trunk Port
Ping from PC1 to Cisco 3725 router's IP address 192.168.10.253
Picture 9 - Ping from PC1 to Cisco 3725
Picture 10 - Captured Traffic on Cisco 3725 Interface FastEthernet0/0
End.
RouterOS Basic Commands
http://rbmikrotik.blogspot.sk/2011/07/mikrotik-router-os-basic-commands.html
RouterOS x86 Features
http://wiki.mikrotik.com/wiki/Manual:RouterOS_features
http://download2.mikrotik.com/what_is_routeros.pdf
RouterOs Switching
http://wiki.mikrotik.com/wiki/Manual:Switch_Chip_Features
http://wiki.mikrotik.com/wiki/Manual:Interface/Bridge#Bridge_Interface_Setup
RouterOS VLANs
http://wiki.mikrotik.com/wiki/Vlans_on_Mikrotik_environment




